When you pick hydraulic fittings stainless steel, 304 and 316 grades are strong and fight rust. Where you use them is important. For example:
- Marine and chemical places need 316 because it lasts longer.
- Industrial or food jobs often use 304 and it works well.
You can trust Kaitu Fitting. Their certified hydraulic fittings stainless steel meet world rules and fit many needs. Talk to our engineers for custom and safe solutions.
Hydraulic Fittings Stainless Steel Grades
304 vs 316 Grades
When you pick hydraulic fittings stainless steel, you look at 304 and 316 grades. Both are austenitic, but they are not the same. 304 stainless steel has iron, carbon, chromium, and nickel. It has at least 18% chromium and 8% nickel. 316 stainless steel has these too, but it also has molybdenum and more nickel. This small change makes 316 work better.
Here is a table to show the main differences:
| Stainless Steel Grade | Key Chemical Components | Chromium Content | Nickel Content | Additional Elements | Corrosion Resistance Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | Iron, Carbon, Chromium, Nickel | Minimum 18% | Minimum 8% | None | Good general corrosion resistance; can pit in chloride environments | Food industry, sanitary hose fittings |
| 316 | Iron, Carbon, Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum | Minimum 16% | Slightly higher than 304 | Molybdenum (added) | Superior resistance to chloride corrosion, pitting, and crevice corrosion | Marine, offshore, chloride-rich atmospheres |
304 is popular because it costs less and works in many jobs. It is used in factories and food places. 316 costs more, but it handles strong chemicals and saltwater better. This makes 316 the best for marine, offshore, and chemical work.
Kaitu Fitting sells both 304 and 316 hydraulic fittings stainless steel. Their products meet DIN, ISO, SAE, JIS, and BSP standards. You can trust their ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications for safety and quality. If you need help, Kaitu’s engineers can help you choose the right grade.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is important when you pick hydraulic fittings stainless steel. 304 stainless steel protects well in most places. But it can rust or pit if it touches chlorides like saltwater or some chemicals.
316 stainless steel has molybdenum, which helps it fight corrosion. It is much stronger against pitting and crevice corrosion in marine and chemical areas. For example:
- 316 stainless steel is best for coastal places, chemical plants, and places with lots of salt or acid.
- 304 stainless steel is good for indoor use, water pipes, and food jobs where there is little chloride.
- 316 can be cleaned often with strong cleaners, so it is great for places that need to be very clean.
Lab tests show 316 stainless steel stays strong and looks good longer in salty or tough places. People who work on boats often pick 316 for anchors, deck parts, and things that touch seawater.
Tip: If your system faces salt, chemicals, or strong cleaning, pick 316. It lasts longer and has fewer problems.
Kaitu Fitting’s hydraulic fittings stainless steel are tested many times to make sure they do not leak and last long. Their certified products help you avoid repairs and downtime. For expert help, talk to Kaitu’s engineers. Kaitu makes stainless steel pipe fittings for plumbing, propane, and fluid systems. If you need custom fittings or advice, their team can help you.
Environment & Application
Operating Conditions
You need to think about where you use hydraulic fittings stainless steel. The place you use them can change how well they work. Here are some things that matter:
- Big changes in temperature can make things weak or hard. Stainless steel fittings work in hot and cold places, from -425°F to 1200°F.
- Wet air or water can cause rust. Stainless steel does not rust easily, so it is good for wet places.
- Saltwater and chemicals can make things rust faster. Grade 316 stainless steel is better than 304 in these tough places.
- Many systems have high pressure. Stainless steel fittings stay strong even if the pressure is over 3000 psi.
Many jobs have these problems. For example, marine and offshore work needs fittings that do not rust in saltwater. Chemical plants use grade 316 because it does not get damaged by strong acids or bases. Food factories need fittings that are safe and clean. Grade 304 is good for most food jobs, but grade 316 is better for salty or sour foods.
Kaitu Fitting gives hydraulic fittings stainless steel to energy, chemical, food, and marine jobs. Their products follow strict rules and pass hard tests, so you can trust them anywhere.
Fluid Compatibility
The kind of fluid in your system is important. Some fluids, like acids, alkalis, or hot oils, can hurt fittings if they are not made from the right stuff. Stainless steel fittings do not react with most fluids and can handle many chemicals. Grade 316 is best for systems with strong chemicals or salty water. Grade 304 works well with water, air, and fluids that are not very strong.
If you pick the wrong grade, your fittings might rust or leak. Always choose the right fitting for the fluid to keep things safe and make them last longer. Kaitu Fitting has special answers for plumbing, propane, and fluid systems. You can ask their engineers for help with special fluids or hard jobs.
Tip: If you want expert help, talk to our engineers. We make stainless steel pipe fittings and can give you custom, safe answers for your needs.
Mechanical Properties
Strength & Durability
When you choose hydraulic fittings, you want them to last and stay strong. Stainless steel fittings give you both. They have high tensile and yield strength, which means they can handle a lot of force before breaking or bending. For example, 304 stainless steel has a tensile strength of 621 MPa, which is a bit higher than 316 stainless steel at 579 MPa. Both grades can take on heavy loads and stress.
Here is a quick look at the numbers:
| Stainless Steel Grade | Minimum Tensile Strength (MPa) | Minimum 0.2% Proof Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | 515 | 205 |
| 316Ti | 515 | 205 |
Stainless steel hydraulic fittings often last more than 50 years, even in tough places like chemical plants or offshore rigs. You do not need to coat them or do much maintenance. They resist rust, pitting, and cracking. This makes them a smart choice for industries like oil and gas, marine, and food processing. Brass and carbon steel fittings do not last as long and need more care.
Stainless steel fittings help you avoid leaks and system failures. You save time and money on repairs.
Pressure Ratings
Pressure ratings tell you how much force a fitting can handle inside a system. Stainless steel fittings work well in high-pressure jobs. They can handle up to 10,000 psi or even more, depending on the design. Carbon steel fittings also work for high pressure, but they do not resist corrosion as well. Brass fittings have lower pressure ratings and are best for low to medium pressure systems.
Here is a table to compare:
| Material | Typical Pressure Rating (PSI) |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Carbon Steel | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Brass | 3,000 – 5,000 |
Stainless steel fittings keep their strength in hot and cold temperatures. They do not get brittle or weak. You can trust them in harsh environments where safety matters most.
Need code-compliant, custom stainless steel pipe fittings for plumbing, propane, or fluid systems? Our engineers can help you find the right solution for your project.
Sizing & Compatibility
System Fit
You need to make sure your hydraulic fittings match your system. The right fit keeps your system safe and working well. If you use the wrong size or thread type, you might see leaks, pressure drops, or even damage to your equipment.
Hydraulic fittings come in many sizing standards. Here are some of the most common ones:
- DIN Metric: Used in Europe and Australia. These fittings use bite-type compression and do not need O-rings.
- JIS Metric: Common in Japan and Korea. These have 30° flare or 60° cone connections.
- Komatsu Metric: Found on Komatsu equipment. These use a special 30° flare.
- SAE: Popular in North America. These use straight threads with O-rings or 45° flare for sealing.
- NPT: Used in the US and Canada. These have tapered threads for a tight seal.
- BSP: Common in Europe and Asia. These come as BSPT (tapered) or BSPP (parallel) threads.
- JIC: Used in high-pressure jobs like aerospace and farming. These have a 37° flare.
Tip: Always measure your fittings with calipers and check the standard before you buy. This helps you avoid leaks and keeps your system running smoothly.
A good system fit also means you follow the right installation steps. Clean the surfaces, line up the angles, and use the correct torque. Do not over-tighten. This keeps your fittings safe and leak-free.
Material Matching
You should match the material of your fittings to the rest of your system. Stainless steel works best when you use it with hoses and parts that can handle the same pressure, temperature, and fluid type. If you mix metals, you might see problems like:
- Chemical reactions that break down seals and cause leaks.
- Galvanic corrosion when different metals touch and moisture is present. This can weaken joints.
- Different wear rates, which can make parts fail sooner.
Note: For code-compliant, custom stainless steel pipe fittings—whether for plumbing, propane, or fluid systems—our engineers can help you find the right match. We offer tailored solutions to fit your needs.
Regular checks and using the right sealants also help your fittings last longer. When you choose the right size and material, you protect your system and make it safer for everyone.
Installation & Process
Machining & Welding
When you work with stainless steel hydraulic fittings, you must be careful with machining and welding. 304 and 316 are hard to machine because they get tougher as you cut them. You should use sharp tools and go slow. This helps make smooth surfaces and good threads. Good threads help stop leaks.
Welding needs special care too. 316L is better for welding because it has less carbon. Less carbon means less rust at the weld. Always use the right welding steps to keep the metal strong. After welding or machining, you should clean the surface with passivation. Passivation uses acid to clean and protect the metal.
Forging is used to make fitting bodies stronger. This helps them last longer. Machining makes threads and sealing surfaces fit just right. Sometimes, heat treatments like annealing help remove stress from forging or machining. You do not need to harden these grades.
Tip: Always check the torque and follow the right steps. This keeps your fittings safe and leak-free.
Fitting Types
There are different fitting types for stainless steel hydraulic systems. Each type has its own way to install and needs certain tools. The table below shows the main differences:
| Fitting Type | Installation Steps | Sealing Method | Pressure Suitability | Tooling Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flare Fittings | Flare tubing with a special tool, assemble sleeve and nut, tighten carefully | Metal-to-metal seal via flared tubing | High pressure and temperature | Flaring tool required |
| Compression Fittings | Insert ferrule, tighten nut to compress ferrule against tubing | Ferrule compresses tubing | Moderate pressure | No special tools, correct nut tightening |
| Bite-type Fittings | Tighten nut to drive ferrule into tubing, creating seal | Ferrule bites into tubing for metal-to-metal seal | High pressure, thick tubing | Torque wrench recommended |
Flare fittings need you to shape the tubing with a flaring tool. These work well for high pressure and heat. Compression fittings are easier to put in. You just tighten the nut, but you must do it right to stop leaks. Bite-type fittings are best for thick tubing and high pressure. You need to use the right torque for a good seal.
Stainless steel fittings do not rust and work in tough places. Pick the fitting type that matches your system and skills.
For expert help, talk to our engineers. We make stainless steel pipe fittings for plumbing, propane, and fluid systems. If you need custom parts or advice, we can help you.
Cost & Availability
Price Comparison
When you pick stainless steel hydraulic fittings, you should think about price and value. The cost changes based on the grade and fitting type. 304 stainless steel fittings are usually cheaper than 316. You can look at the price ranges in this table:
| Fitting Type | Stainless Steel Grade | Price Range (USD) | Application/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Fittings | 304 | Few dollars up to $20 | Simple fittings like straight couplings, plumbing |
| Medium-Complexity Fittings | 304 (commonly) | $20 to $100 | Hydraulic systems, secure connections |
| High-Performance/Specialized | 316 | Starting from $100 up to several hundred dollars | Demanding industries, premium corrosion resistance |
304 fittings are good for most jobs and cost less money. 316 fittings cost more because they fight corrosion better and last longer in hard places like marine or chemical plants.
You might pay more at first for stainless steel fittings than for carbon steel or brass. But stainless steel fittings last longer and need less fixing. Over time, you save money because you do not need to replace them as much.
Market Access
You can buy stainless steel hydraulic fittings in many places around the world. Suppliers like Kaitu Fitting have lots of choices, so you can find the right part for your system. Stainless steel fittings come in many sizes and thread types, so they fit your equipment easily.
When you think about the total cost, look at more than just the price. Stainless steel fittings, especially 316, help you avoid expensive repairs and lost work time. They stop leaks, rust, and damage from shaking. Over ten years, you can save a lot on repairs and downtime.
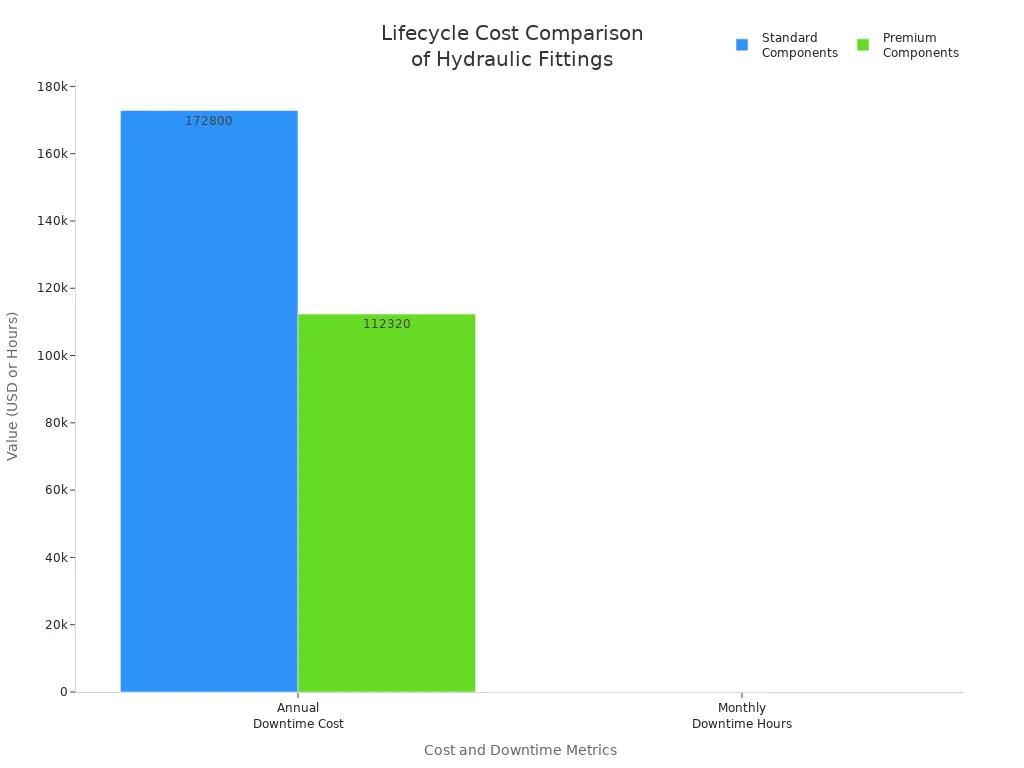
The chart above shows that premium stainless steel fittings lower downtime and save money each year compared to regular fittings. Even though you pay more at first, you get better value over the life of your system.
Need a custom solution or expert advice? As a stainless steel pipe fittings maker, we offer special, code-compliant answers for plumbing, propane, and fluid systems. Our engineers can help you pick the right fittings for your needs.
Supplier & Certification
Quality Standards
When picking hydraulic fittings stainless steel, you should check for good quality standards. ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 are two main certifications to look for. ISO 9001 helps companies make safe and steady products. It gives rules for how suppliers do their work and get better. IATF 16949 is for the car industry. It makes sure every fitting is safe and high quality.
Many top suppliers follow these rules. They test each fitting with special checks. These checks include looking for cracks, measuring size, and testing strength. Some companies use smart machines to measure every part and keep records for each group. This helps you trust your fittings will last and work well.
Here are some standards you should know:
- ISO 9001: Makes sure products are safe and work well.
- IATF 16949: Used for cars and tough jobs.
- SAE, DIN, CE, EN, GB: Other rules for safety and how things should work.
Tip: Always ask your supplier about their certifications. Certified suppliers give you better products and fewer problems.
Reliable Sourcing
You want a supplier who always gives you the right hydraulic fittings stainless steel. Good suppliers use strong metals and smart machines. They test each fitting for leaks and pressure. They put codes on each part so you can see where it came from. Good suppliers also make custom fittings and help you pick the best one.
Look for these signs of a good supplier:
- Runs their own factory and controls all steps.
- Has many types and sizes of fittings.
- Gives technical help and quick answers.
- Uses barcodes and batch codes for tracking.
- Delivers on time and helps after you buy.
- Follows world rules for safety and quality.
Kaitu Fitting is a trusted maker of stainless steel pipe fittings. You can talk to their engineers for expert help. They give custom, code-safe answers for plumbing, propane, and fluid systems. You can get special fittings, CPVC parts, and advice for your job.
For safe and strong hydraulic fittings stainless steel, pick a supplier with good certifications and a record of quality.
When you pick stainless steel grades for hydraulic fittings, remember these things: Look at how well the grade fights rust, especially if you use it near the ocean or with chemicals. Choose a grade that matches your system’s pressure, temperature, and fluid type. Make sure the fittings have safety and quality certifications. Think about how much the fittings will help you over time, not just what they cost now.
Ask certified suppliers like Kaitu Fitting for help and advice. You will get strong products, good support, and feel safe. If you want expert help, talk to our engineers. We make special, code-compliant fittings for plumbing, propane, and fluid systems.
FAQ
What is the main difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel fittings?
304 stainless steel is good for most uses. 316 stainless steel has molybdenum added. This helps it fight rust from saltwater and chemicals. Pick 316 if you need fittings for tough places.
Can I use stainless steel fittings with any type of fluid?
Stainless steel fittings work with many fluids. 316 stainless steel is best for strong chemicals and saltwater. Always check if your fluid matches the fitting before you buy.
How do I know which thread type my system needs?
Look in your equipment manual or use a caliper to measure threads. Some common thread types are NPT, BSP, JIC, and metric. The right thread type helps stop leaks and damage.
Why should I choose certified suppliers for hydraulic fittings?
Certified suppliers follow strict quality rules like ISO 9001 and IATF 16949. This means you get safer and longer-lasting fittings that meet industry standards.
Need a professional solution? Contact our engineers. We make stainless steel pipe fittings for plumbing, propane, and fluid systems. If you need custom fittings, CPVC parts, or expert help, we are here for you.
